What is Factitious Keratoconjunctivitis ? |
Factitious Keratoconjunctivitis is a difficult diagnosis to make and is often missed when not suspected. It should be considered in any case in which sustained trauma occurs in poorly explained or suspicious circumstances. The term factitious disorders describe conditions where physical findings are intentionally produced by person to assume sick role.
Factitious disorder most commonly occurs during second or third decade of life, and more often among health professionals. Factitious disease affecting eyes is commonly seen in nasal or inferior quadrant of the eye. Topical anaesthetic abuse is one of the most common self-induced injuries to the eye.
We, as clinician, tend to find aetiology underlying any eye disease. Therefore, self-inflicted injuries often do not draw attention. Self-injuring patients often reach out for help but are incapable of describing what help is required. Failure in diagnosis of such disease may delay therapy to prevent permanent damage.
Factitious disorders must be distinguished from malingering and somatoform disorders. In malingering, in addition to intentionally induced physical features, there is always evidence of external incentive. Malingering may be adaptive as in prisoners of war, and does not necessarily mean psychopathology. Somatoform disorders produce clinical findings which are not fully explained. Somatoform disorders include conditions such as hypochondriasis and hysteria.
Factitious Keratoconjunctivitis Symptoms |
Symptoms may be disproportionate to the clinical signs. Patients usually seek multiple medical advises over an extended period of time. These may be with varying complaints and from different treating physicians.
Patient may present with
- Dermatitis on eyelids.
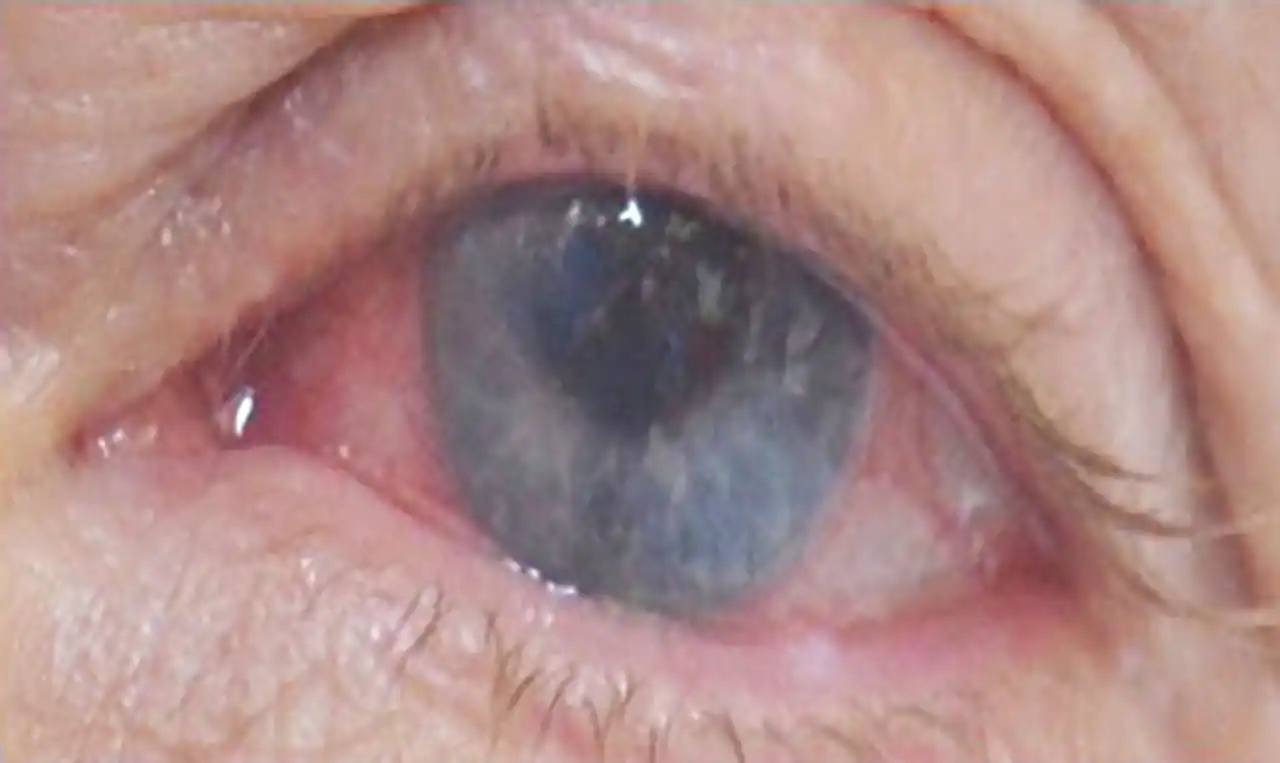
- Keratoconjunctivitis with features such as redness, photophobia and copious discharge.
- Unconcerned attitude of the patient
Factitious Keratoconjunctivitis Causes |
Conjunctival inflammation in factitious keratoconjunctivitis is produced by self-inflicted physical or chemical injury. It may occur in context of a psychiatric illness.
Self-inflicted injury in and around eye is rare and not usually sight threatening in children. However, it may be a warning sign of much more serious problem of physical or sexual abuse.
Factitious keratoconjunctivitis in adults is often associated with complex psychological or emotional problem.
Self-inflicted injury may be in the form of
- Chemical injury.
- Use of medication.
- Mechanical injury such as corneal abrasion or laceration.
Causative agents may include topical anaesthetic agent, acid, or even pieces of chalk.
Factitious Keratoconjunctivitis Diagnosis |
Diagnosis depends upon clinical features since history of self-inflicted injury may not be available. Differential diagnosis helps in reaching to a conclusive diagnosis.
Patient may show presence of chronic, usually over three weeks, of conjunctivitis having peculiar features such as
- Presence of purulent discharge.
- Localisation of conjunctivitis, usually in the inferonasal quadrant of the eye which stains with rose bengal dye.
- Superior bulbar conjunctiva is usually not involved.
- Severe hyperaemia.
- Mild chemosis.
- Punctate keratopathy.
- Linear corneal abrasions.
- Persistent corneal epithelial defects.
- Presence of pseudodendrites.
- Sterile ring infiltrate and hypopyon.
- Secondary infection with Candida.
- Corneal scarring.
- Focal corneal perforation (rare).
